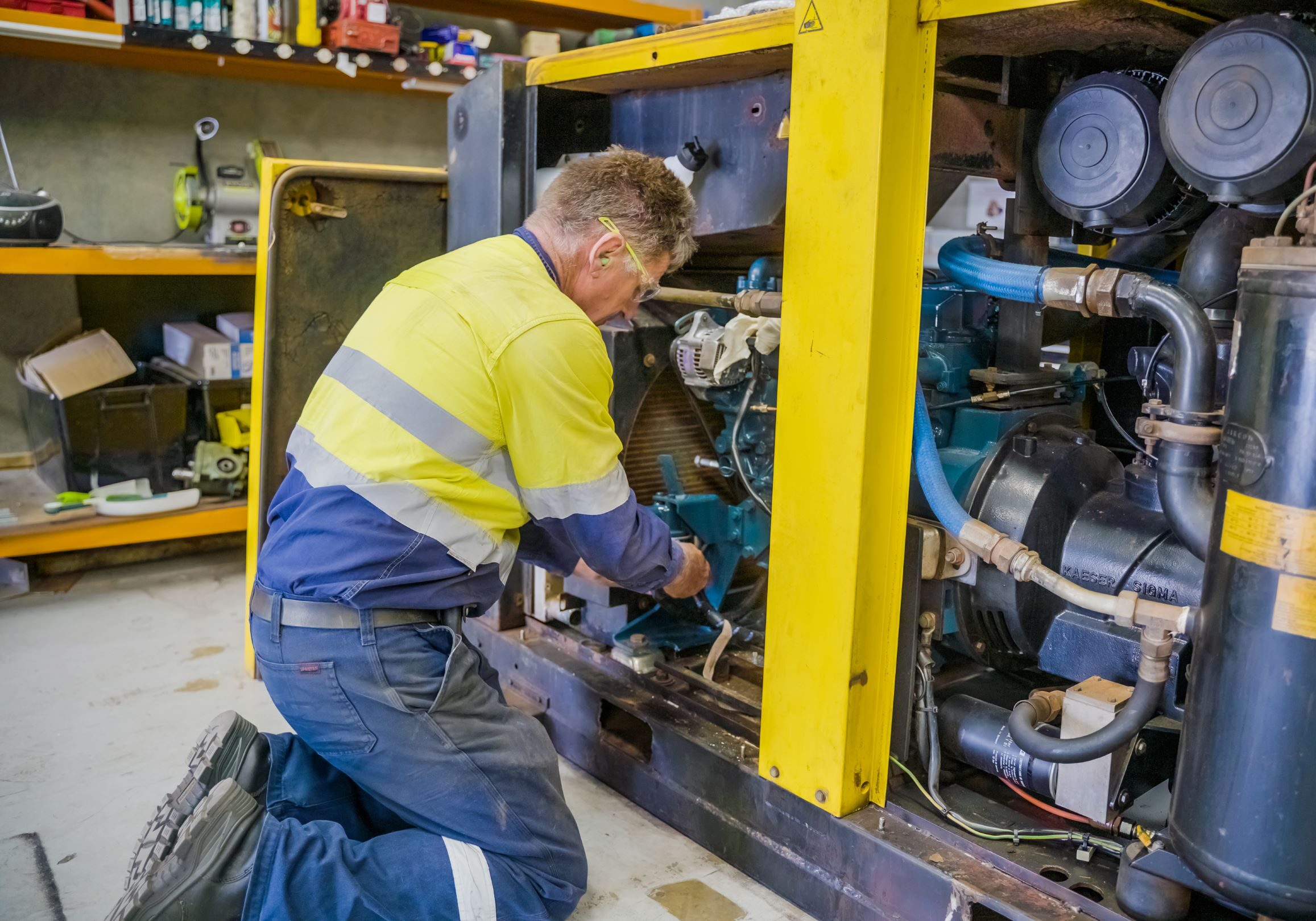
Improve compressor performance, efficiency and compliance with our technical bulletins
Download our technical bulletins for practical information on compressor components, system performance, and maintenance recommendations. Each bulletin is designed to help you make informed decisions and keep your compressed air system running efficiently.
Compressor accessories: Dryers, separators, receivers and drains
Your compressor’s separator, dryer and drains work together to control or eliminate moisture and oil in your system.
Servicing and replacing these accessories as recommended ensures clean, dry air for your operations.
Cooling systems: Intercoolers, aftercoolers, hoses and thermostats explained
The cooling components of your compressor help control the temperature of both the system and the air it generates, so it’s important to maintain these elements according to your compressor’s maintenance schedule.
Your compressor’s intercooler should be cleaned regularly, checked for leaks and replaced as recommended.
Electrical components: Motors, contactors, switches and controllers overview
Electrical components are the heart of your compressed air system and are the elements that control your machine, so they should be serviced and maintained according to manufacturer specifications.
They provide and help control the energy used to generate compressed air, so it’s important to maintain and replace these elements as recommended.
Inline filter elements: Replacement and exchange program guide
Replacing your compressor’s inline filter elements improves the efficiency of your compressed air system because your compressor is not losing pressure or having to work as hard to do its job.
Regular replacement of your compressor’s filter elements also reduces contamination levels, improving the safety of your operations.
Valves in compressed air systems: Inlet, minimum pressure, solenoid and more
The lifespan of your compressor’s valves depends on usage and maintenance. Over time, valves and seals wear down and may need to be replaced or refurbished, based on a technician’s assessment.
This is typically recommended when there are signs of failure, reduced performance, or when the components exceed the manufacturer’s recommended operating hours.
Airends: Rebearing vs. replacement – What you need to know
Rebearing or replacing your compressor’s airend at the end of its service life can improve performance, reduce energy consumption, and minimise downtime.
It can also ease the load on the motor, helping to extend its lifespan when carried out as recommended.
Compressor and dryer location guidelines for best performance
Your compressor and dryer should be installed in an area that is: clean, dry, free from dust, well ventilated, away from direct heat, and easily accessible for service and maintenance.
Installing your compressor in the correct location will save you time and money. You’ll reduce breakdown, servicing and repair costs and extend the life of your compressed air system.
Air receiver standards: sizing, compliance and safety requirements
Pressure vessels used in the workplace can be potentially dangerous, with the risk of failure and explosion causing property damage, injury and even fatality if not suitably maintained.
It’s essential to properly install, service and inspect compressed air receivers, ensuring that all equipment complies with the relevant Australian Standards and WorkSafe WA regulations.
Heat recovery systems: Reduce energy waste in your compressed air system
Air compressors, particularly larger industrial models, generate significant heat as a byproduct of air compression. Without a heat recovery system, this energy is usually wasted.
By installing an aftermarket heat exchanger, fitted by our compressed air technicians, you can recover up to 85% of the heat produced by your system.
Breathing air testing requirements for compressed air systems
In many industrial and production environments, compressed air is essential not only for powering equipment but also for providing clean, breathable air for staff.
Regular testing is required to ensure worker safety and to confirm that your respiratory protection complies with Australian Standards and is used correctly.
Oil-water separators: filtering contaminants to help meet environmental regulations
Like any industrial process, compressed air isn’t immune to contaminants. An oil-water separator is an accessory installed as part of your compressed air system which helps manage the moisture and oil vapour produced through the process of compressing air.
An oil-water separator improves efficiency, reduces the risk of equipment damage, helps lower operating costs, and supports your business in meeting environmental regulations.
Fixed speed vs. variable speed drive (VSD) compressors: Pros and cons
Variable Speed Drive (VSD) is an advanced technology used in compressors that helps businesses reduce energy wastage and improve efficiency.
VSD compressors are designed to automatically adjust their output based on your exact air demand – boosting efficiency and reducing energy costs.
Pressure safety valves: ensuring your system operates within safe pressure limits
A pressure safety valve (PSV) is a valve which automatically releases air from the receiver tank if internal pressure exceeds a safe limit – preventing dangerous overpressure that could cause the tank to rupture – or in extreme cases, explode.
The PSV plays a critical role in ensuring your compressed air system always operates within safe pressure limits.